Gearing Up for the 6G Era
The exponential potential of next-generation networks promises to accelerate the transformation of business and society.
The past few decades have featured some of the most groundbreaking technological innovations in human history. The world is now heading toward another landmark event: the launch of 6G.
“Transformational” is the word Peter Vetter, President of Nokia Bell Labs, uses to describe the next generation of mobile networking, which is touted to be 10 times faster than its predecessor, 5G.
But the next generation of mobile networks will go beyond simply offering faster internet and communication speeds. 6G’s ubiquitous connectivity will fuse the digital and physical worlds, ultimately changing the way we work and communicate with one another.
The commercial rollout of 5G began in 2019 and continues today. It has given users a glimpse of what high speed connectivity and lower latency can achieve, including powering smart cities, factories, the Internet of Things (IoT) and robotics.
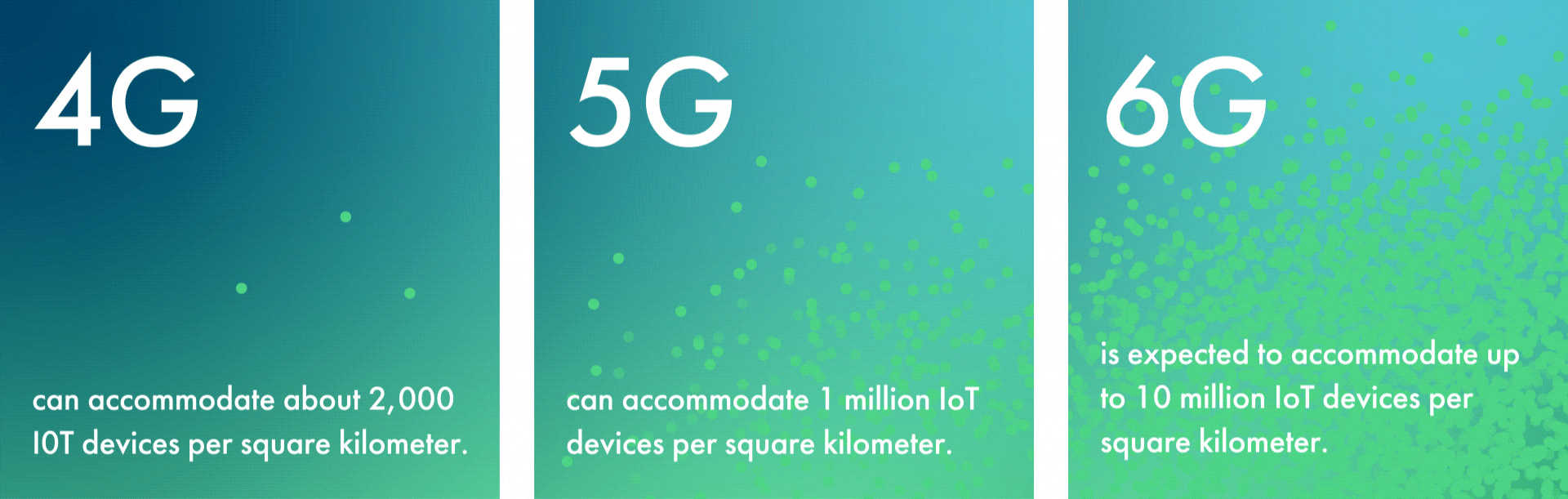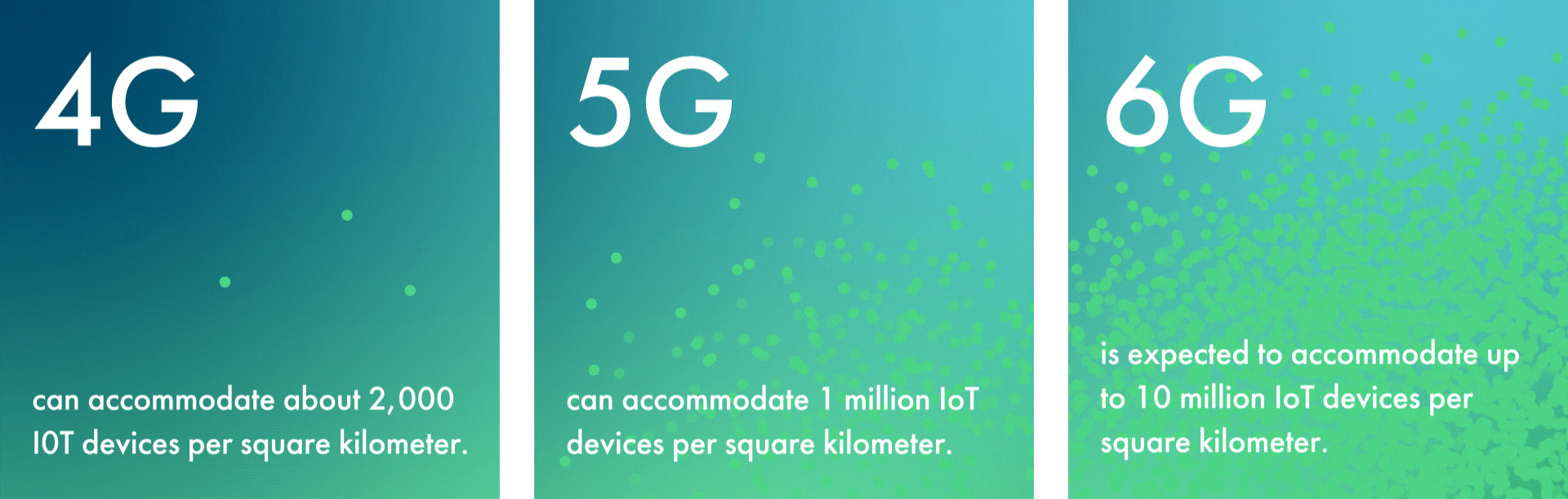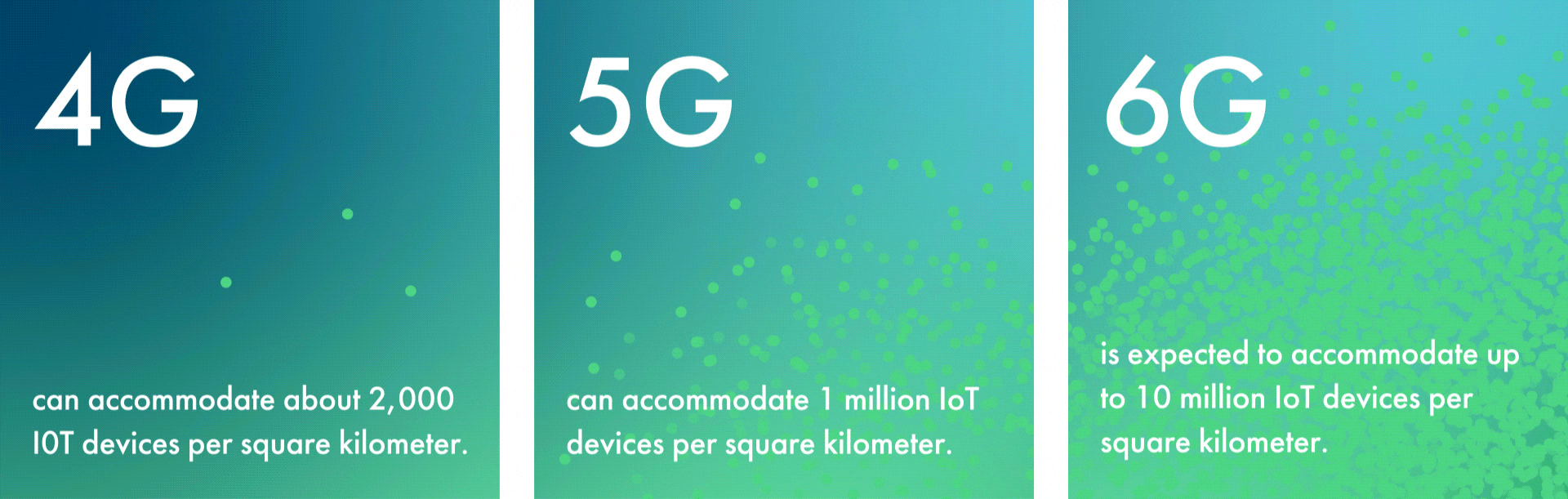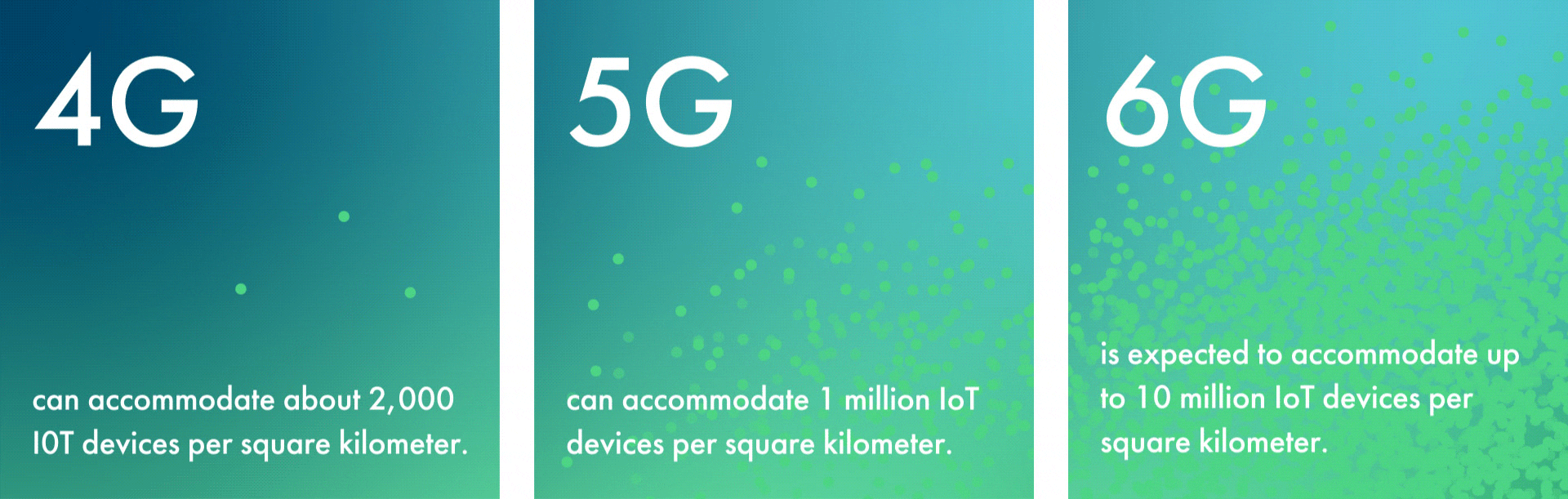
While 5G’s capacity is vast, 6G’s will be truly exponential. For example, 6G is expected to accommodate up to 10 million IoT devices per square kilometer. This is a tenfold increase from 5G’s limit of 1 million—and an astronomical increase over 4G’s limit of about 2,000 devices per square kilometer.
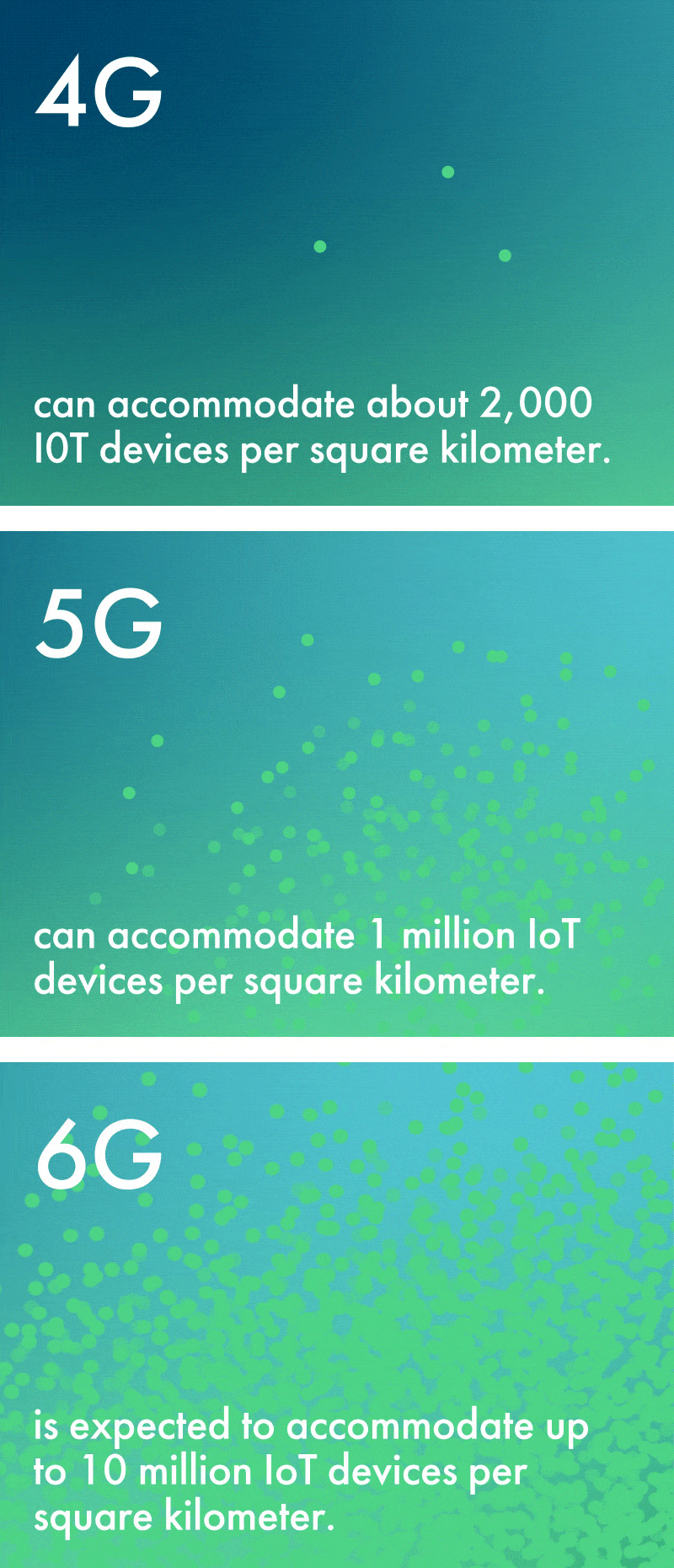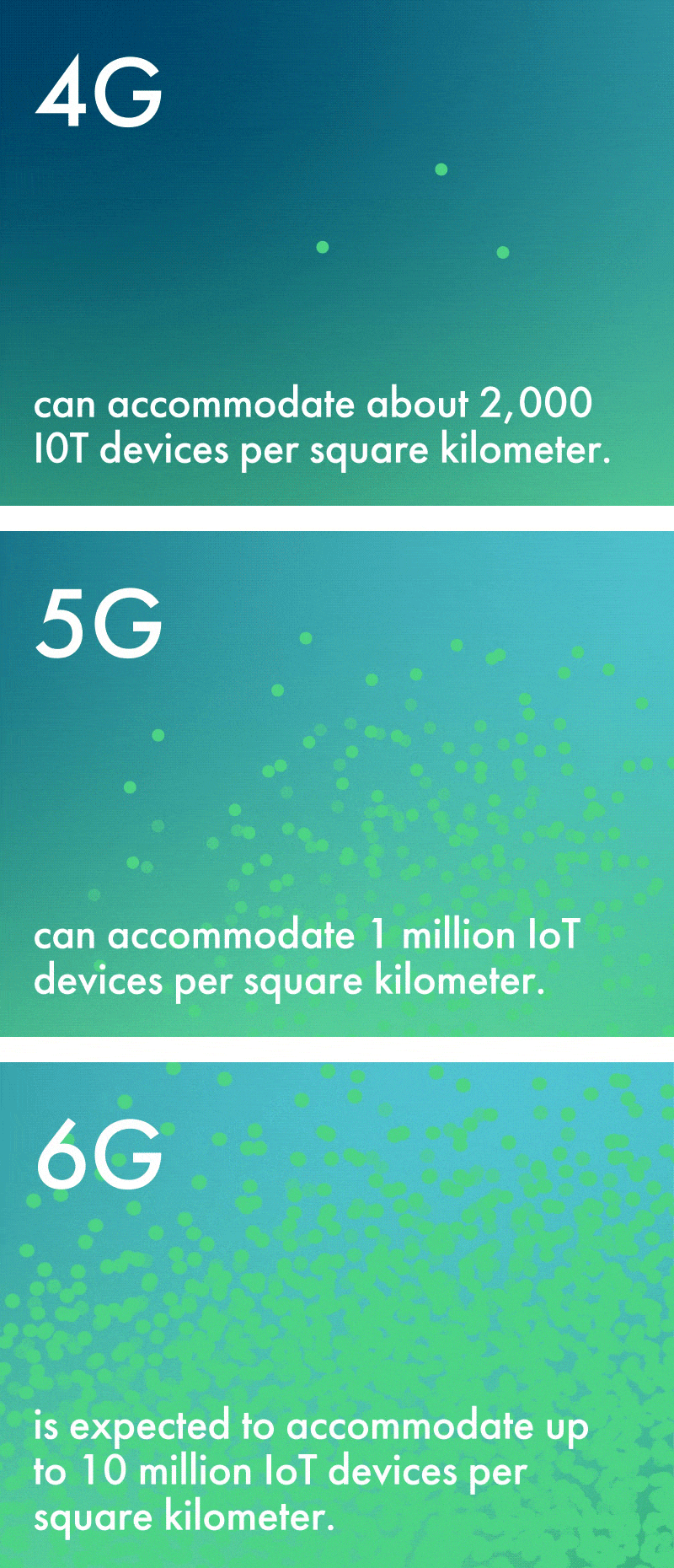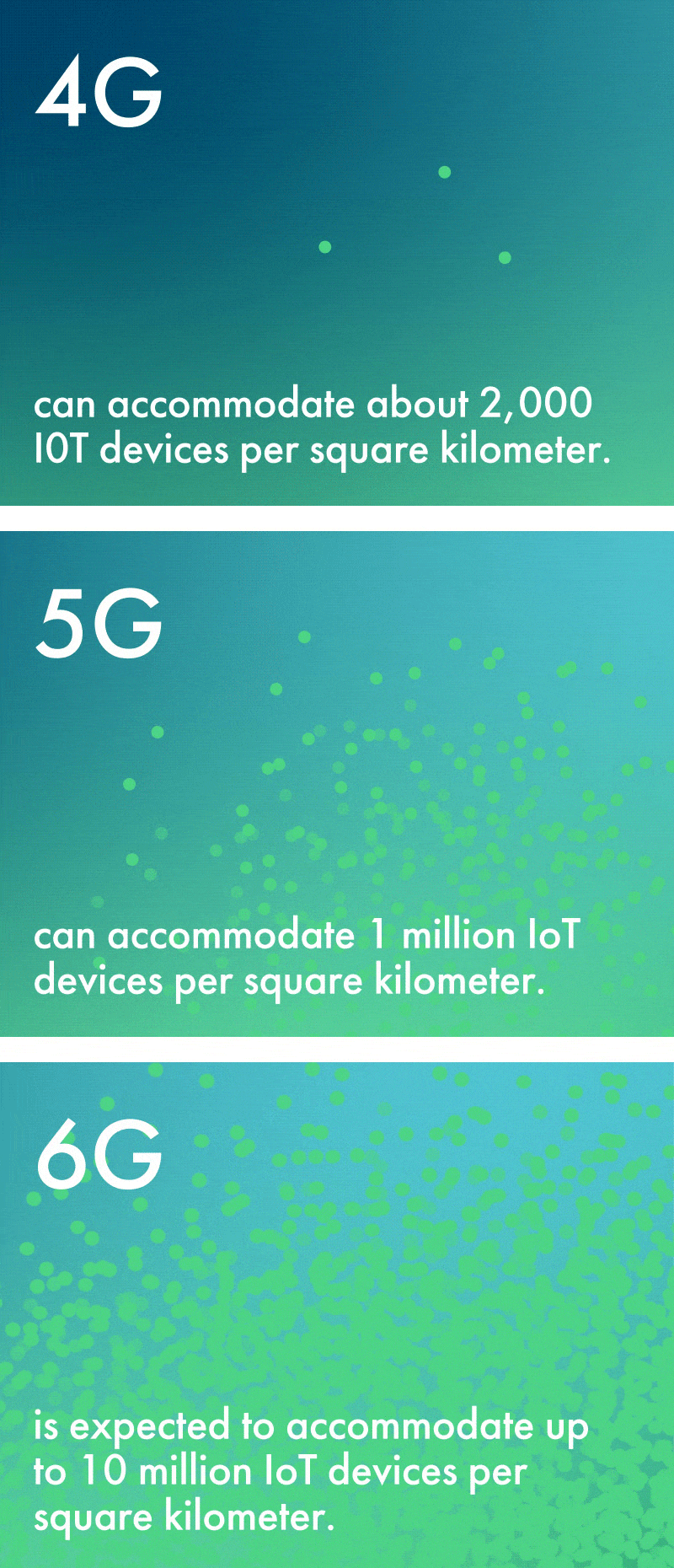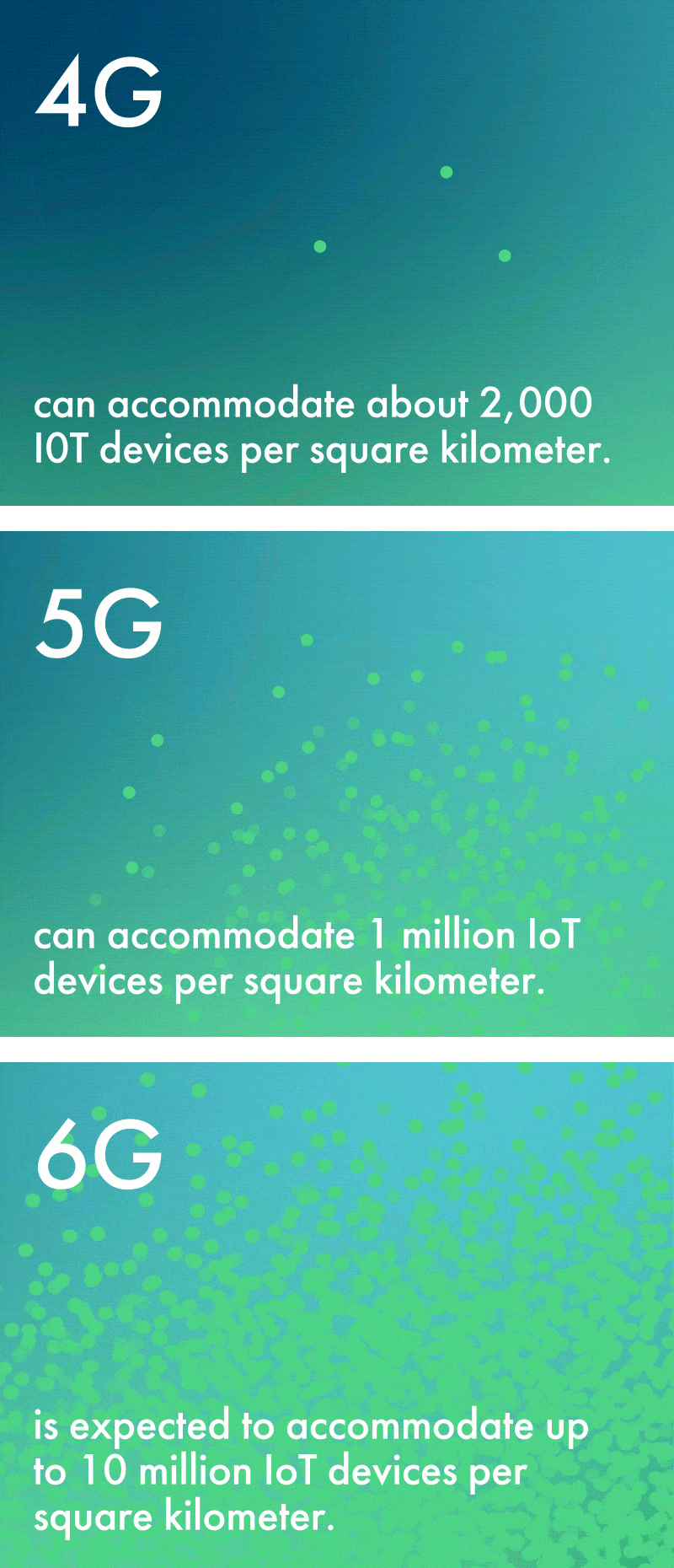
Because of the widespread proliferation of IoT devices it will enable and the enhanced sensing capabilities of the network, 6G is sometimes referred to as the ‘network with a sixth sense’ – and this creates new opportunities across numerous industries. Farmers can utilize environmental sensors to monitor crop systems and weather patterns with enhanced precision. Patients can be monitored by health care professionals in real time by biological sensors connected to the network. Factories with connected devices become safer and more efficient, with greater remote control of machinery.
And while 5G continues to be deployed globally, businesses are eager to understand the potential of 6G and the additional value it will bring to unlock new opportunities. As such, organizations around the world are investing increasing amounts of time and money in 6G R&D to be ready for the next wave of transformation.
Tim O’Farrell, Chair Professor of Wireless Communications at the University of Sheffield, is a leading expert in the field. He describes 6G as a significant leap forward.
“The provision of these [6G] technologies across industries will enable them to do more and purchase services over the network in a bespoke way, defined to their needs,” he says.
The first 6G networks could roll out as early as 2028. By 2030, 6G is expected to be commercially available.
Vetter and his team are at the forefront of 6G research. “This year, we’ve seen very significant progress—the first tangible moves based on the concept,” he says. “We like to be 10 years ahead of the curve, so we already started defining the research direction for 6G four years ago.”


Andreas Mueller, Project Director of 6G at Bosch, is working closely with Nokia Bell Labs to take the next steps toward 6G and shape what this innovation will look like, particularly within different vertical domains. “6G will play an important role in areas like mobility, manufacturing and digital twinning, with almost endless possibilities,” he says. “Especially its completely new capabilities.
“[For example] the integration of sensing capabilities and native support for artificial intelligence will turn a mobile network from a mere connectivity infrastructure to a full-fledged application enablement platform. This will provide significant value-add and further accelerate the digital transformation of our economy and society,” he says.
Health care is one sector that will particularly benefit from this technology. 6G-enabled digital twinning will allow researchers to rapidly test new treatments in a virtual environment before conducting a full clinical trial. This can accelerate the drug development process and create personalized treatments while reducing costs.

Vetter is excited about these technological advancements. “We’re looking into future applications like industrial automation—how we can use enhanced sensing technologies, and combine them with radio sensing and other IoT sensors to create real-time digital twins of our physical world in a digital environment,” he says.
With 6G, digital twin models of entire cities and other settings will be deployed on a much broader scale, with much higher precision and realistic accuracy, delivering unparalleled insights and unlocking new and improved planning and growth strategies.
The past few years have seen a whirlwind of digital innovation, especially as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) emerge as trailblazers in automating workflows and revealing new possibilities.
“AI is expected to play a very big role in 6G, both in terms of running the network and the services delivered on the network,” says O’Farrell.
6G networks will leverage AI and ML to create a dynamic “air interface” that will determine the most efficient transmission routes for devices to communicate with one another. This will reduce latency, as the air interface continually adapts to its changing environment, hardware and applications.
“We’ve shown how AI can improve the capacity of the mobile radio system by immediately learning the channel and adapting to the channel, and do that 30% better than a state-of-the-art technology,” Vetter says, adding that this is an “industry first.”
AI itself stands to benefit from the capacity, compute and speed that 6G will deliver, boosting AI’s ability to retrieve and process large amounts of data in real time.
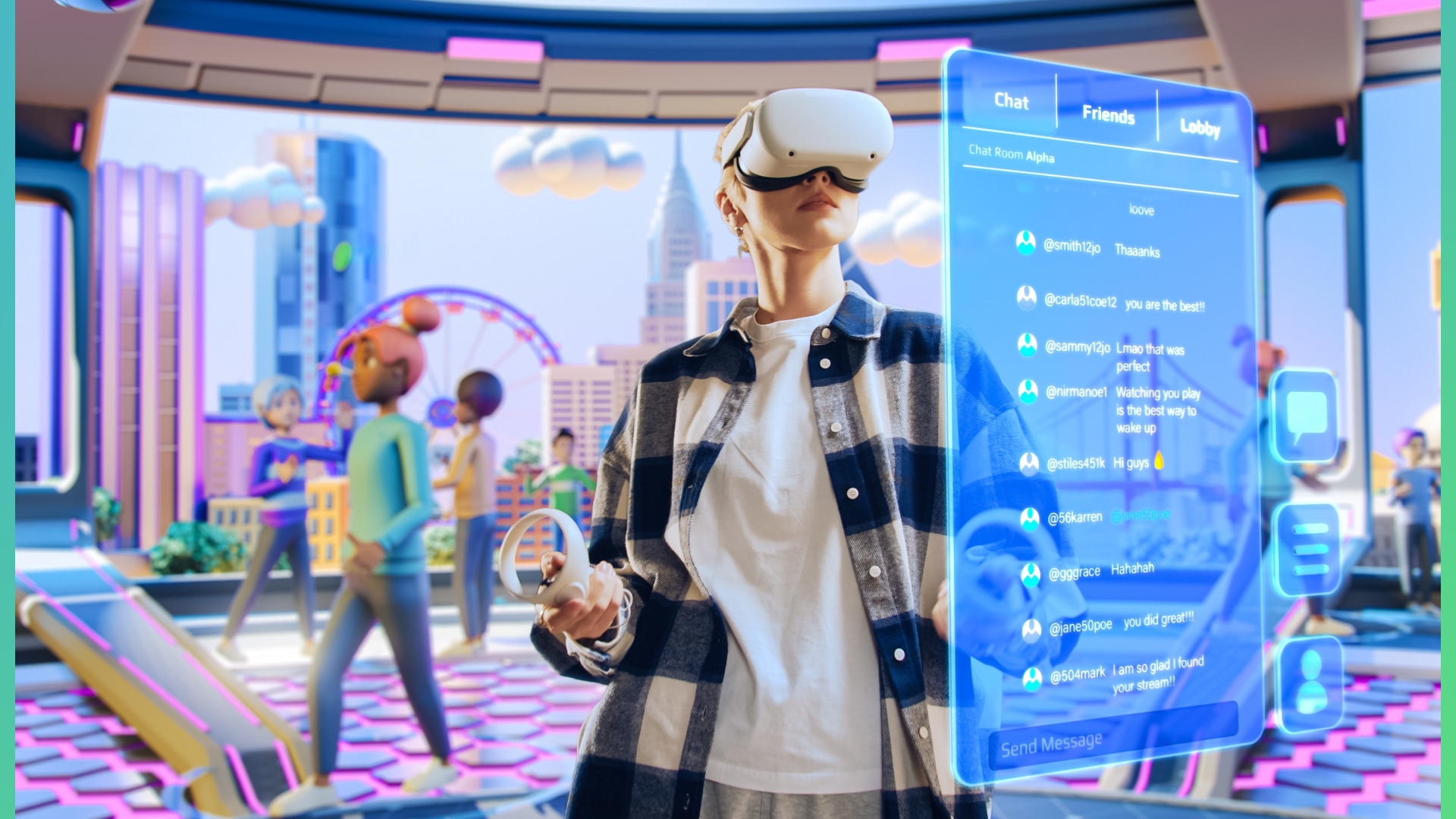
These benefits extend to the metaverse, where lower latency and faster data processing speeds will provide a smoother, more immersive user experience. With the support of 5G, strides are already being made toward a digital-physical system, and 6G promises to realize an unfettered synchronization of both worlds.


Energy efficiency also plays a significant role in the 6G world.
“Traffic goes up by a factor of 20 to 30 in a decade,” Vetter observes. “At the same time, you don’t want energy consumption to go up by that same order of magnitude.”
6G’s improved ability to turn off components and scale down capacity at times of lower demand will be critical in improving energy efficiency. However, there remains a need for technological innovation to achieve net zero for this new network technology. Nokia Bell Labs is exploring a range of solutions that include liquid cooling and adaptive waveforms to reduce energy consumption.
The innovation required to bring 6G online is huge, and the shift toward sustainability is one of the many ways in which corporations are striving to shape the future of telecommunication networks.
“I see 6G as the major platform for future innovation,” Mueller says. “The best is yet to come.”
