4 Ways
Reducing H2O Use
Cuts CO2 Emissions

World’s
Annual
Freshwater
Usage
1/3
150 Companies
+ Supply Chains


Just 150 companies and their supply chains account for one-third of the world’s freshwater used annually, according to an internal study by the Water Resilience Coalition, a consortium of 35 companies that have committed to reducing their water use.













































Move Less Water
The interior surfaces of a manufacturing facility’s production system will need to be cleaned on a regular basis, often using clean-in-place (CIP) technology, where by the equipment doesn’t need to be disassembled. That cleaning process needs to be monitored closely to verify cleanliness and to ensure facilities don’t move more hot water through the system – and use more energy to heat it – than is necessary.
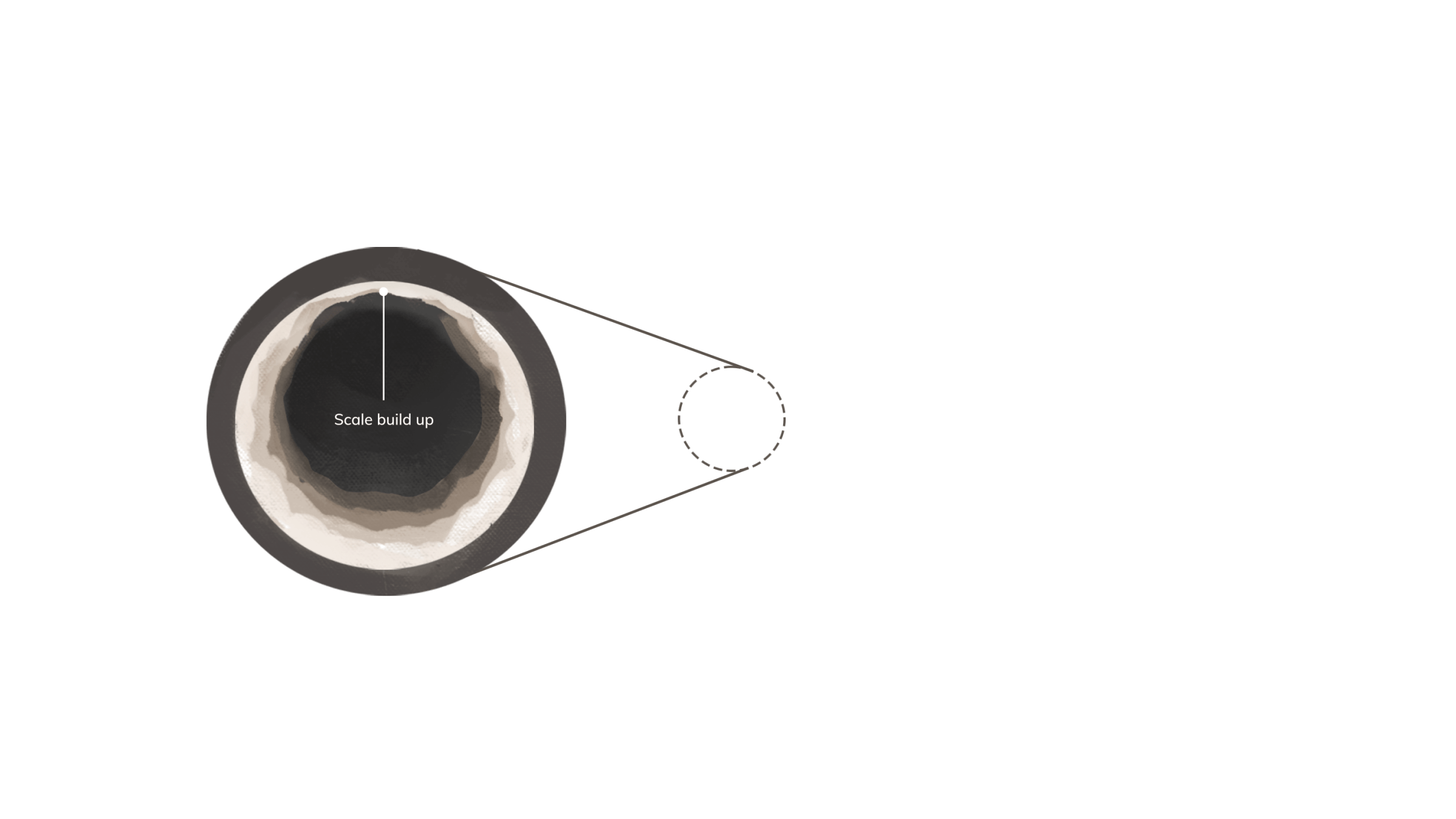
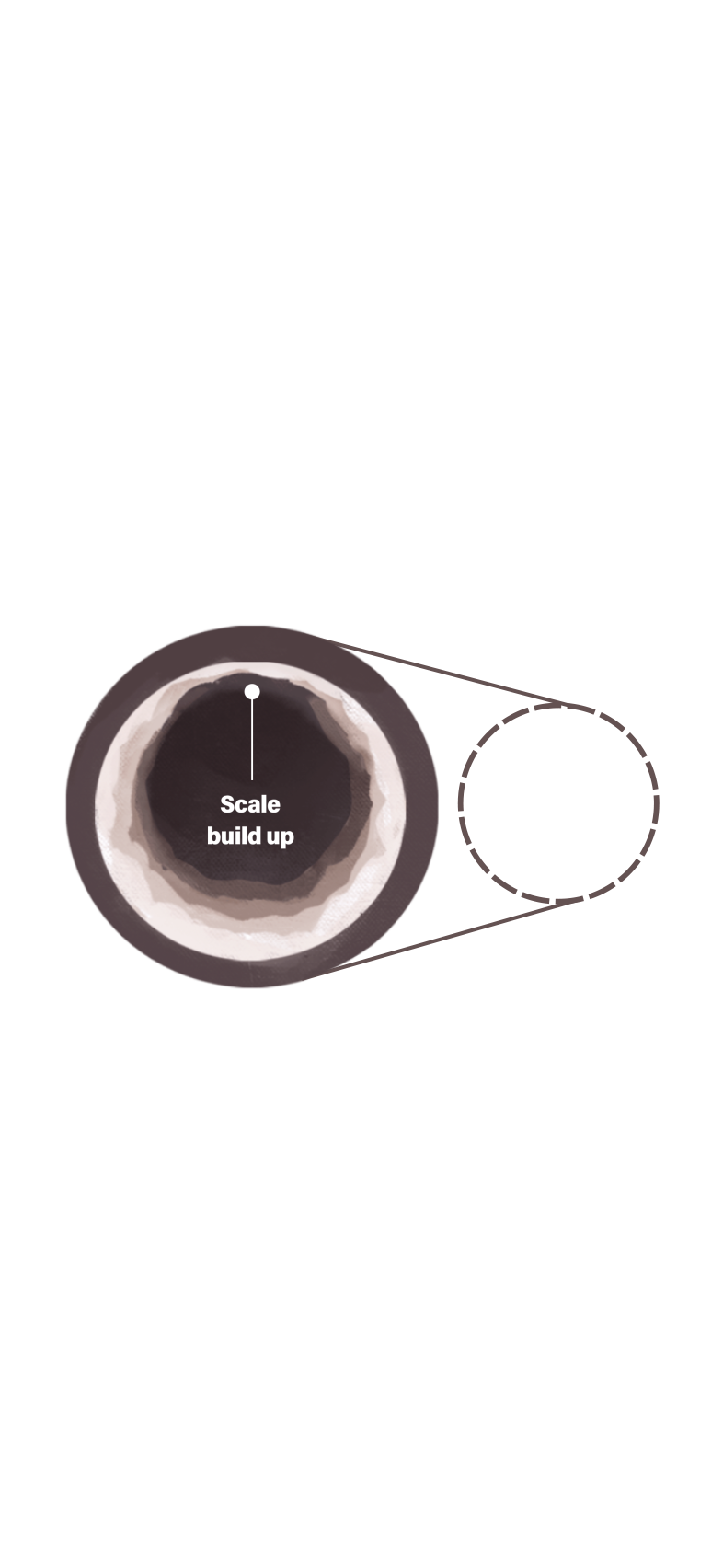
Heat Less Water
Heating water can produce scale inside a boiler. The boiler then requires more energy to operate. To lessen scale formation, water should be pretreated before using it in the boiler system by removing solids and reducing its mineral content. Properly treated, this already heated water can be recycled through boilers several times, reducing total water and energy usage.
Cool Less Water
Cooling systems throughout the plant use water to reduce the temperature of a product or process, such as fermentation or pasteurization. Treating this water keeps the cooling efficiency high and by reusing it a cooling system reduces the amount of water needed.
Treat Less Water
Before water that has been used for heating, cooling and cleaning is released back into the environment, it will be treated again. “But we’re able to take some of that wastewater, after it’s been purified, and use it again,” Emanuel says.
consumption
use
gas emissions
“You’re helping preserve the world’s water supplies, while at the same time you’re cutting your expenses and you’re one step closer to net zero carbon emissions,“ says Emanuel.
“It’s a win-win-win. But first you must transform the way you think about water.”



