
A Smarter Power Grid Can Help Create a More Sustainable World
Learn how 5G and edge computing will accelerate the energy transition in the third installment of “The Imagination Exchange,” a series co-created by Ericsson and Bloomberg Media Studios.
Information and communication technology solutions can enable a reduction of global carbon emissions by up to 15 percent by 2030, according to Ericsson Research.
For example, the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing can help energy companies in their renewable energy transformation, achieving both operational excellence and environmental sustainability.
In fact, the 15 percent estimation was done before technologies like 5G and edge computing were rolled out. Now Ericsson believes that government and industries can do even more.
5G, the fifth-generation wireless cellular network, will be the foundation for realizing the full potential of technologies like IoT because 5G helps control more devices remotely in applications where real-time network performance is critical.
In its 2022 Ericsson Mobility Report, Ericsson forecasts that with 5G, the number of IoT connections will more than double from 14.6 billion in 2022 to 30.2 billion in 2027.
“5G and cellular technology could soon contribute to an exponential acceleration of global efforts to reduce carbon emissions.”

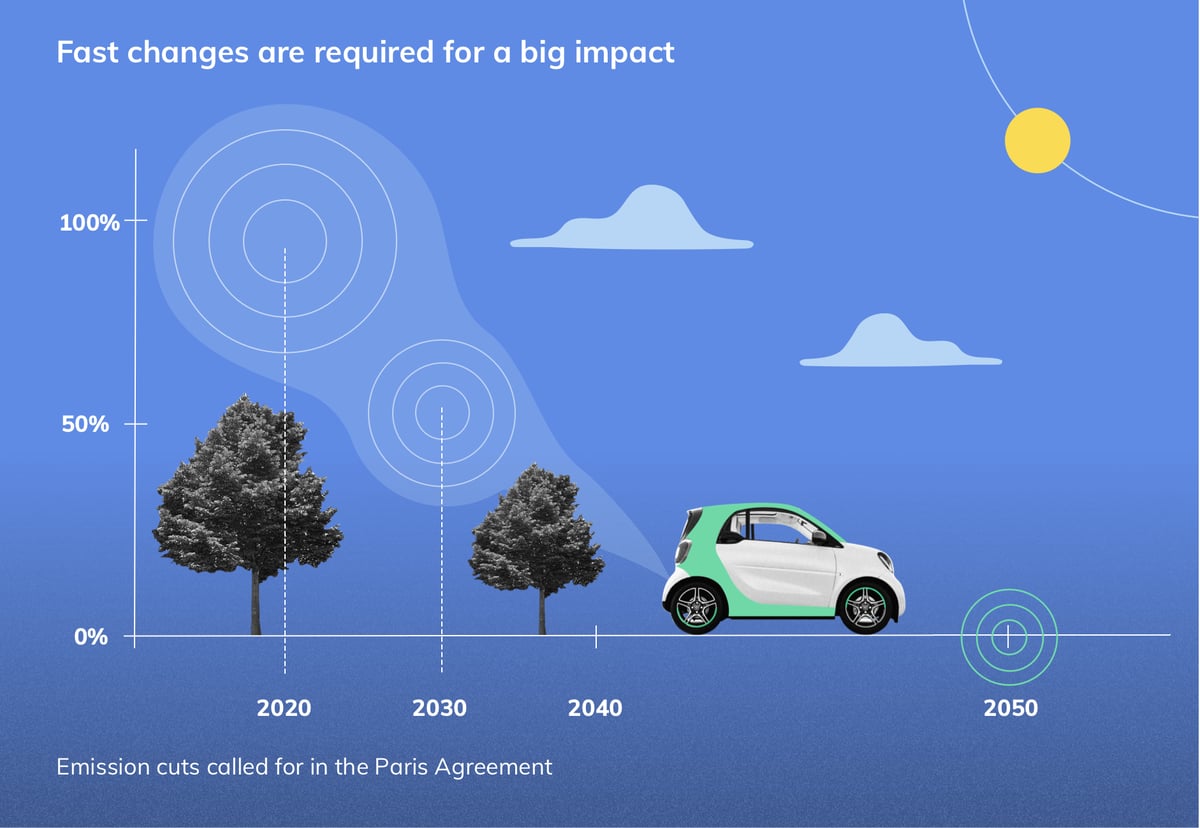
Science shows that to avoid the worst impacts of climate change and maintain a livable planet, the global temperature increase needs to be limited to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. But the Earth’s average temperature is already about 1.1°C warmer than it was in the late 1800s.
To keep global warming to no more than 1.5°C—as called for in the Paris Agreement—emissions need to be cut by 45 percent by 2030 and reach Net Zero by 2050. This critical effort to reduce the environmental, physical and economic damage due to climate change requires transformational steps by governments and industries worldwide.
More than 1,200 companies have implemented science-based targets in line with Net Zero, and more than 1,000 cities, 1,000 educational institutions and 400 financial institutions have joined the United Nations’ Race to Zero, pledging to take significant, immediate action to halve global emissions by 2030. Additionally, over 60 countries and nearly two-thirds of Fortune Global 500 companies have set a target for Net Zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
Opportunities for the greatest impact involve the biggest contributors of greenhouse gasses. The manufacturing, transportation and energy sectors combined are responsible for almost two-thirds of all greenhouse gas emissions, according to Exponential Roadmap, a cross-sector study which Ericsson Research is a part of.
“We need to tackle these three sectors, and that will require significant transformation,” says Tamsons. “We need fast changes from these big industries.”
Ericsson harnesses power of connectivity for a better world
Ericsson believes in a world where limitless connectivity improves lives, redefines business and pioneers a sustainable future. In the technology sector, Ericsson is leading the way.
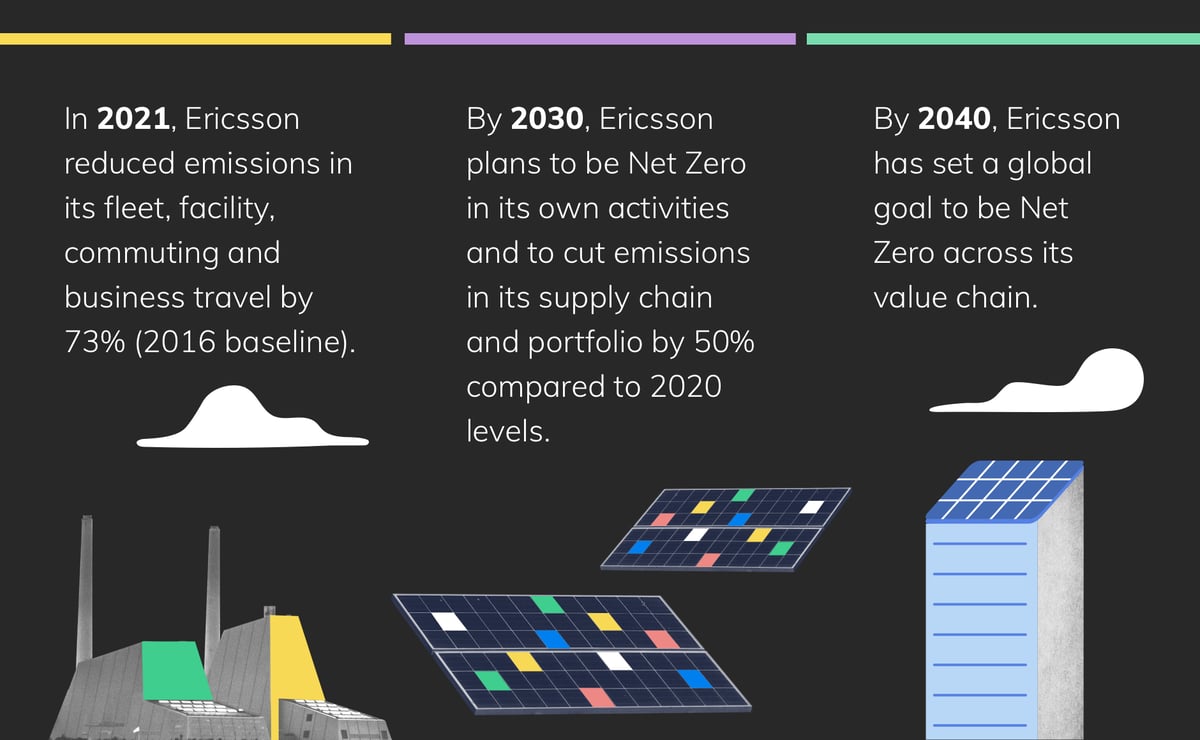
5G and technology pave a path to Net Zero
Digitalization, 5G and other cellular technologies can play a vital role in helping industries reach Net Zero emissions. More efficient transportation and manufacturing, optimized renewable energy systems and low-carbon transportation are just some of the benefits.
The energy, manufacturing and transport sectors’ decarbonization efforts could benefit the most from digitalization and 5G. Across these industries, increasingly interconnected supply chains, transportation and energy networks could use connectivity to increase operational efficiencies and productivity, and virtuous cycles of shared data and insights could optimize systems for lower resource usage and carbon emissions.
“Decarbonizing Industries with Connectivity & 5G,” a report created by the MIT Insights Review and sponsored by Ericsson, highlights that 5G and other digital cellular technologies would help these industries to connect and manage disparate and remote assets, resulting in reduced costs, improved outputs and lower carbon emissions.
5G-enabled technologies like IoT would enable the creation of a smarter power grid that offers flexibility in both supply and demand and a responsive network in which both production and usage can be quantified in real time.
5G will be critical for the future of renewable energy, as it provides higher levels of reconfigurability for power grids—which may allow local networks to work separately from the main network, helping renewable energy installations operate more dynamically and efficiently.
“The power grid of the future is going be a customer-centered grid, which means everybody will have an active role.”
Monti is working with Ericsson and other partners on automating the power grid. He says that 5G will be important for enabling renewable energy, smart technologies and the new grid.
“The traditional power grid was based on big power plants, but the future will see customers having small devices connected at the edge, and that's where connection with IoT can make a difference,” he says. “5G infrastructure is the best solution to achieve efficient automation for the grid of the future.”

Source: Ericsson Research
“We believe that the digitalization of society, powered by technologies such as 5G, will be fundamental to halve emissions every decade. We have demonstrated solutions that help make it possible; now it’s up to companies and policymakers to act by scaling these solutions to enable an exponential reduction of carbon emissions globally.”
Watch the Video
The Imagination Exchange: Smart Grids and a More Sustainable World
Watch Monti and Tamsons exchange ideas for a more sustainable world.
