Today's healthcare innovations confront persistent patient care challenges by targeting previously untreatable conditions and leveraging a myriad of groundbreaking approaches. Genomic medicines provide transformative treatments for complex conditions. Advanced diagnostics enable earlier disease detection, while personalized medicine tailors interventions to individual patient profiles, optimizing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing adverse effects. And preventive therapies increasingly target chronic illnesses, using novel approaches to both prevent and reverse them.
This transformation reflects a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms, enabling previously unattainable interventions, such as antibody drug conjugates delivering chemotherapy directly to cancer cells, and genomic medicines repairing genetic defects at their source. With pharmaceutical R&D spending forecast to reach $340 billion by 2030 — a 17% increase from today — companies are strategically pivoting toward sophisticated therapeutic modalities that address some of the most challenging medical conditions.1
Next-Generation Treatments Are Transforming Patient Care
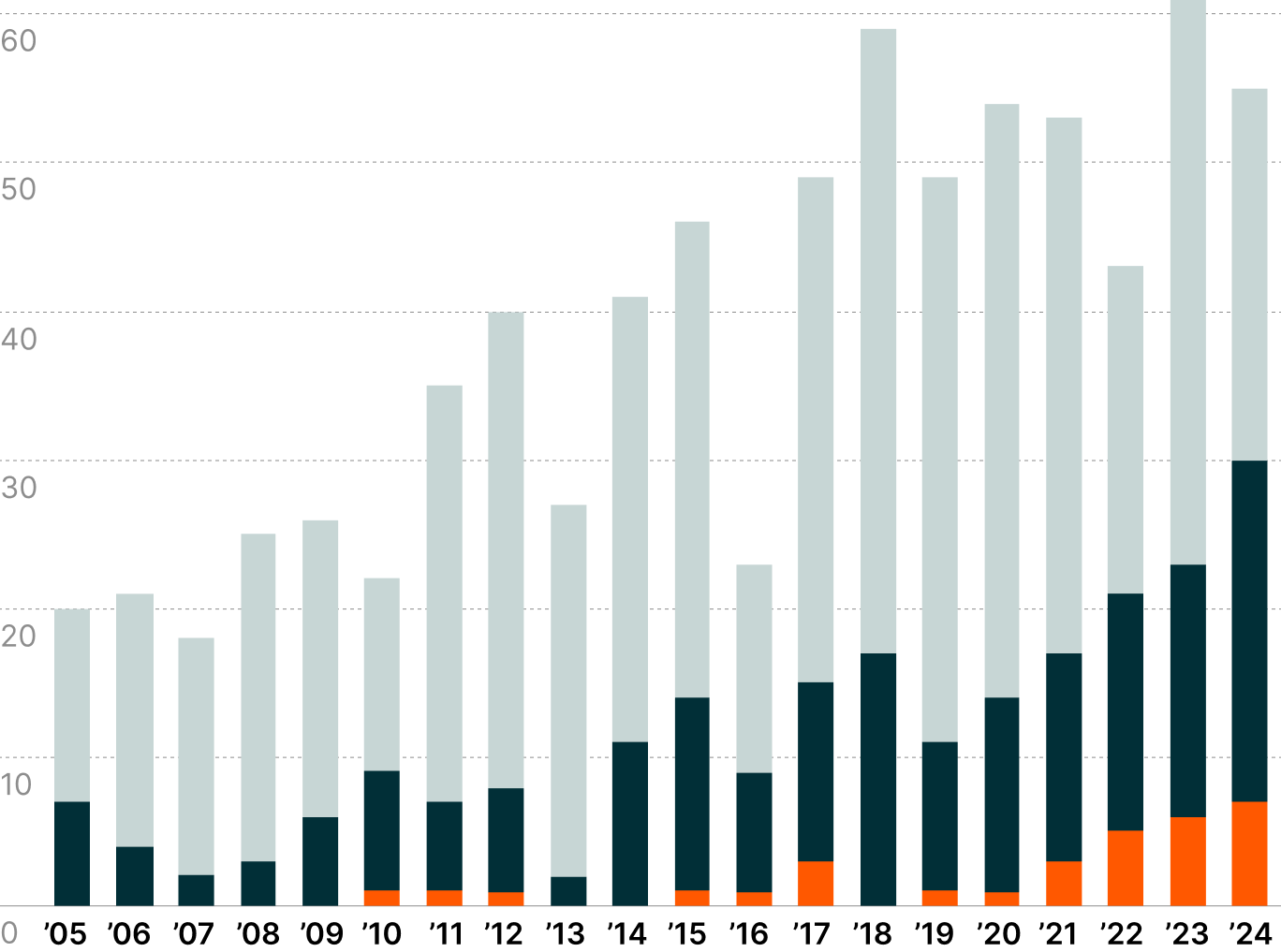
The pharmaceutical landscape is undergoing a profound paradigm shift as the medical community gains access to increasingly sophisticated treatment arsenals across disease categories. While small molecule drugs maintain their dominance in FDA approvals, the growing emergence of large molecule biologics and genomic medicines signals growing acceptance of more complex therapeutic modalities.
This evolution unfolds against a backdrop of mounting industry pressures. As blockbuster drugs account for an estimated 80% of new drug revenue, competitors aim to accelerate and streamline R&D.2
FDA Approvals by Drug Category3
Small, simple chemical structures that are usually administered orally.
aka BiologicsMade from living cells, tissues, and viruses. They are administered via injections or infusions.
Represent the cutting edge of medicine, using living cells and genetic modifications to repair, replace, or restore damaged tissue and treat illnesses.
Balancing Risk and Opportunity Across the Treatment Landscape
Certain pockets of medical R&D are expected to disproportionately benefit from these newer treatment modalities due to unmet medical needs, the size of affected patient populations, and historical success in treating the illness.
Medical specialties cluster differently across four quadrants, as some offer steady returns and others promise transformational but uncertain outcomes. Companies typically balance success rates against peak sales projections when allocating R&D resources across these opportunity zones.
Risk vs. Return Analysis by Medical Specialty4
Size of Bubble: Market size, based on estimated worldwide 2030 sales.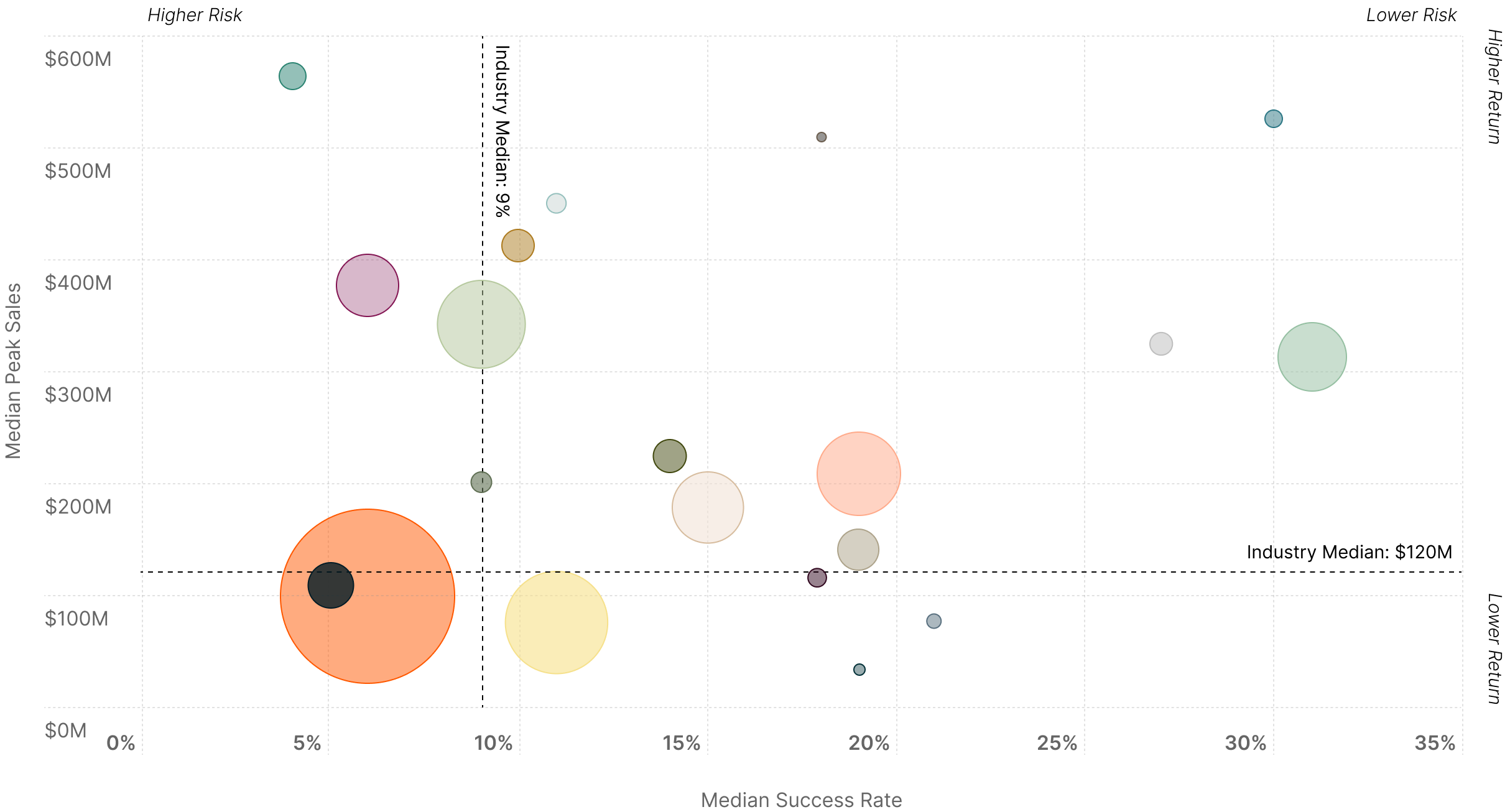
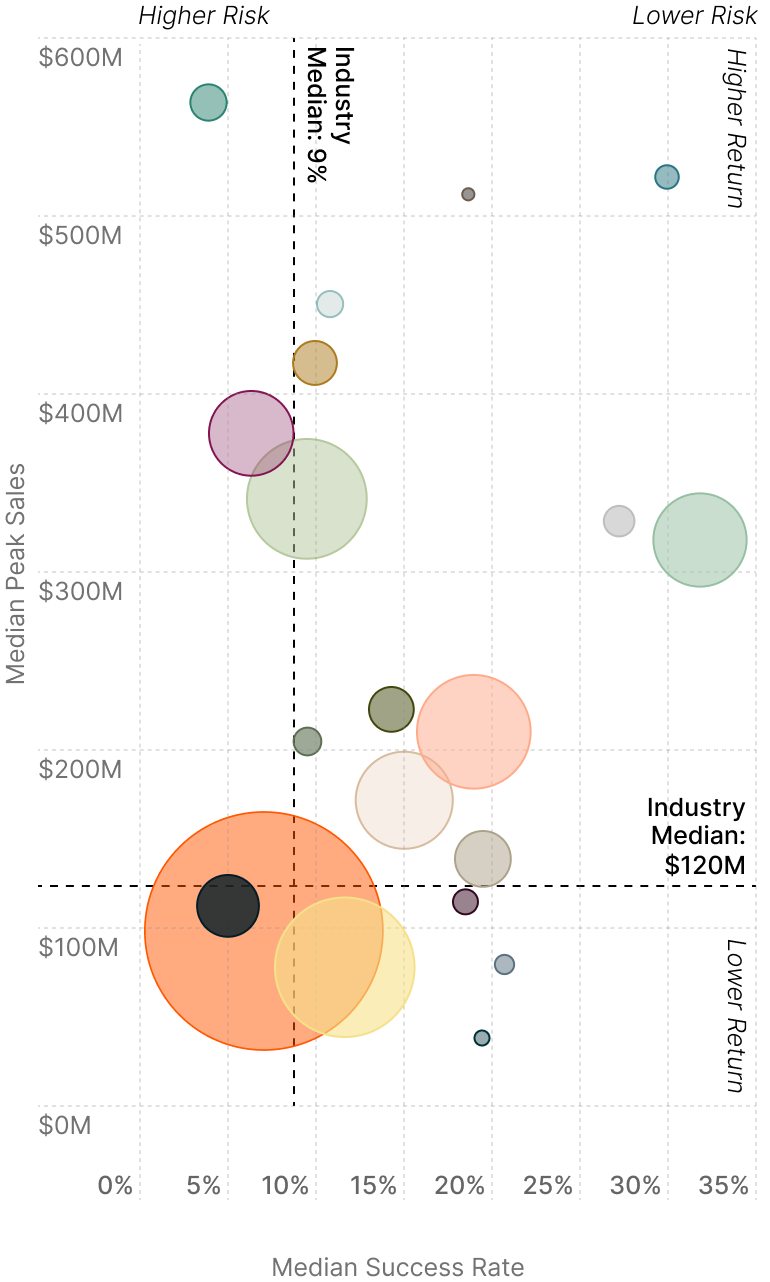








































MS = Multiple Sclerosis
NSCLC = Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
SCLC = Small Cell Lung Cancer
Revolutionizing Multi-Disease Treatment
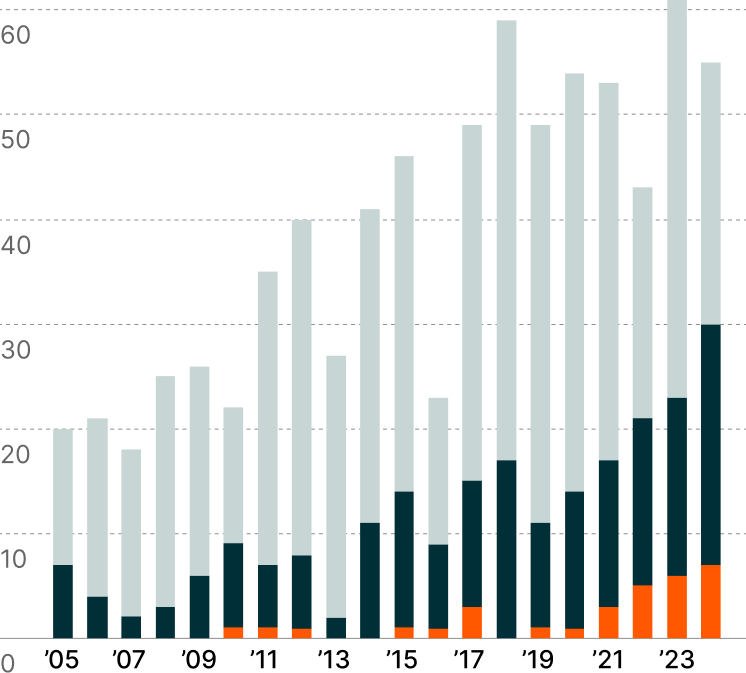
Originally developed for diabetes, GLP-1 treatments have achieved weight reductions of up to 22.5%, realizing outcomes comparable to bariatric surgeries through pharmaceutical intervention alone.5 Based on the category’s impressive adoption, companies are systematically expanding GLP-1 applications across interconnected metabolic disorders such as MASH, chronic heart disease, and chronic kidney disease.
Each newly approved indication strengthens the scientific foundation supporting GLP-1's therapeutic relevance, while expanding the addressable patient universe. GLP-1 treatments, including Ozempic, are expected to achieve $183 billion in annual sales by 2032, marking the fastest-growing therapeutic modality in the pharmaceutical sector.6 This trajectory exemplifies how breakthrough treatments can transcend their original therapeutic applications to redefine possibilities in medicine and create entirely new market paradigms.
GLP-1 Revenues by Indication7
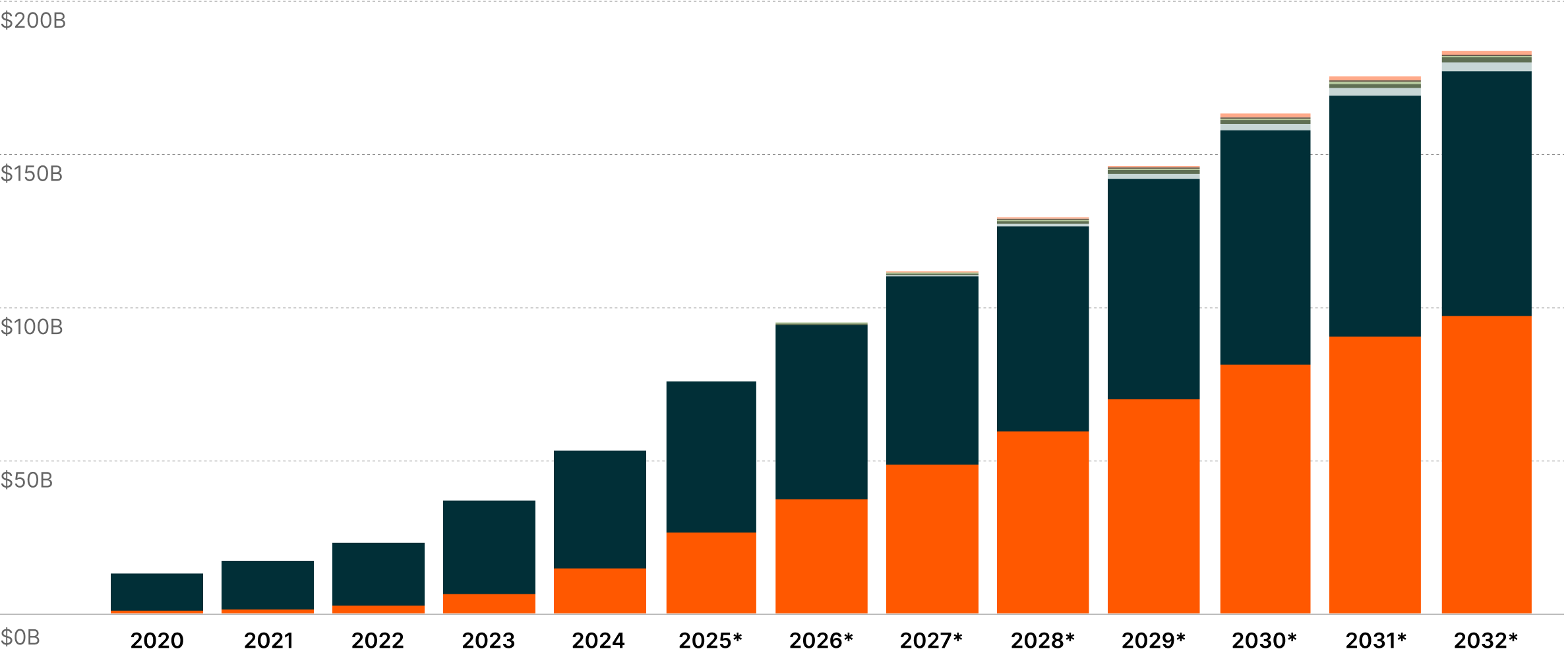
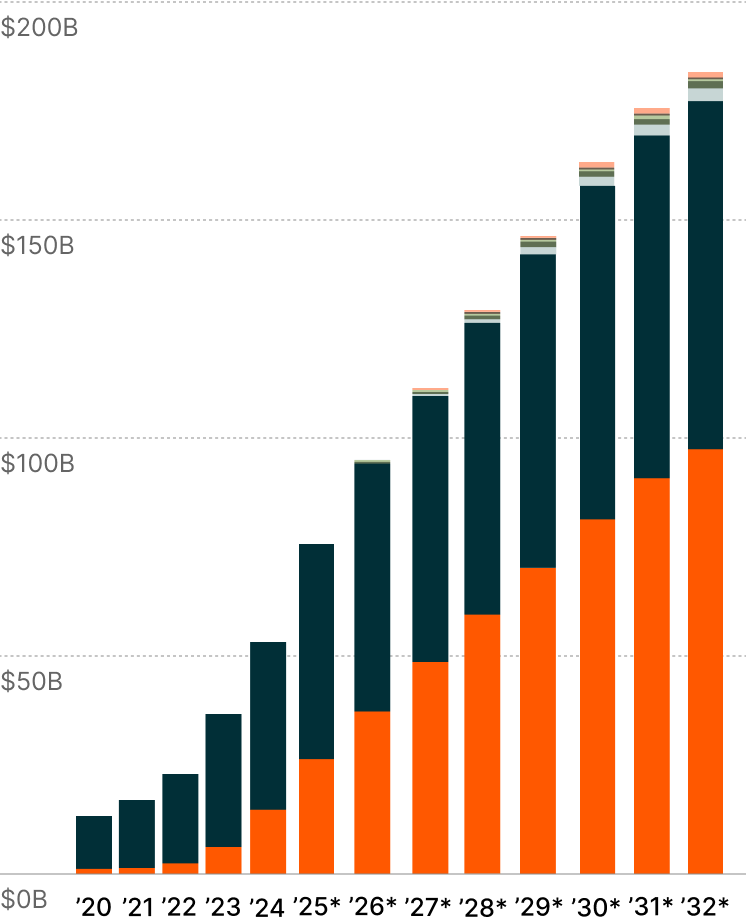
MASH = Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis
EXPERT TAKEAWAY
“A new era of medicine is emerging. Biotechnology is turning once-untreatable conditions into manageable ones, while precision therapies reshape patient care This is not incremental change — it's a fundamental reimagining of how we prevent, treat, and even reverse disease.”






