As tensions around the world continue to escalate, nations seek to modernize their capabilities and strengthen their defense tech arsenals. Ongoing conflicts highlight the power of advanced defense systems, prompting the global defense industry to embrace rapid innovation. Cutting-edge technology increasingly shapes modern warfare, making one thing clear: The most advanced systems often determine strategic outcomes.
A sustained global defense spending boom now targets technology-driven solutions, accelerating adoption of AI, autonomous drones, and sophisticated cybersecurity across military organizations worldwide. This expansion aims to increase technological superiority, as strategic advantage shifts toward innovations that demonstrably serve as deterrents in current conflicts.
Global Conflicts Drive Military Modernization
The 61 active conflicts around the world in 2024 — the highest number since World War II — have encouraged the global defense industry to continue shedding its historic resistance to commercial technology.1 Against this backdrop, global defense spending hit a record $2.7 trillion in 2024 and is projected to reach $3.6 trillion by 2030.2
This growth trajectory reflects a fundamental reassessment of security priorities amid rising geopolitical tensions. Even traditionally neutral nations are increasing their defense budgets. The spending surge extends beyond traditional military powers, with countries across Europe, Asia, and other regions modernizing their armed forces in response to evolving threats.
Military Expenditure by Region & Global Military Burden3
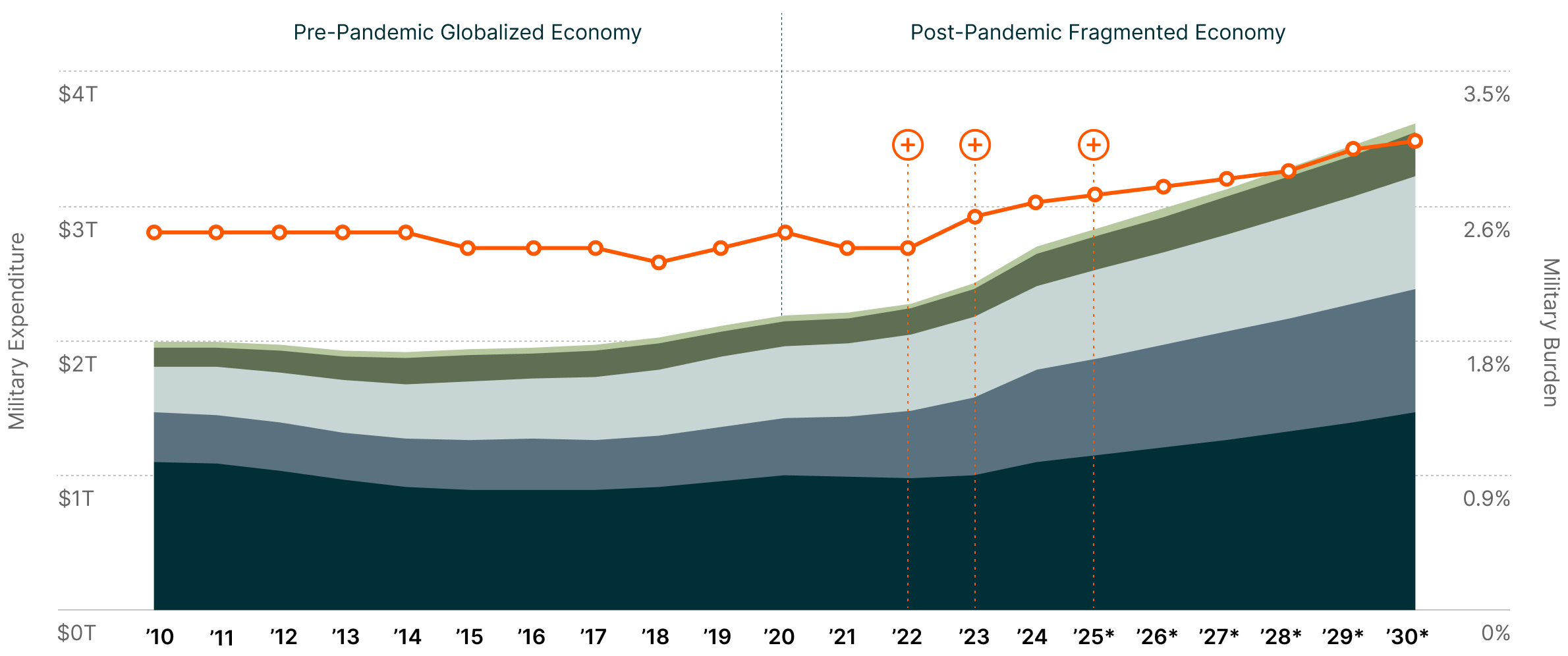
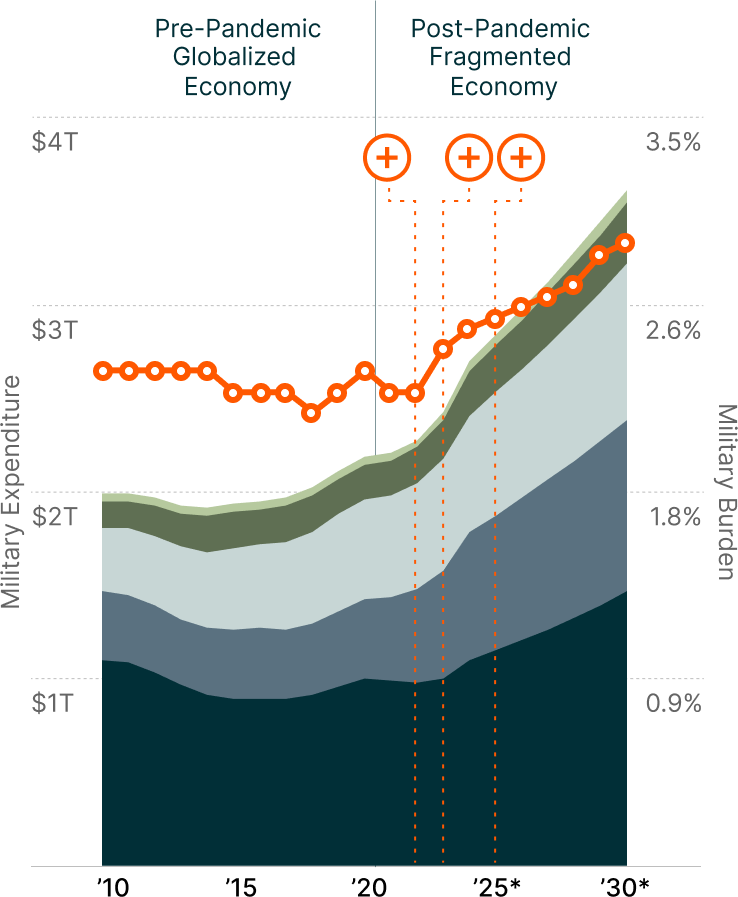
Note: Military burden refers to the proportion of GDP allocated to military expenditures.
NATO Spending Targets New Defense Tech
Only 18
of NATO’s 32 members met the 2% GDP defense spending target in 2024.7
NATO’s historic 2025 agreement to significantly boost military spending shows the global commitment to defense modernization. Member nations pledged to raise their annual defense target from 2% of GDP to 5% by 2035, potentially adding hundreds of billions of dollars in annual expenditures.4
European countries account for a significant share of this increase, with EU NATO members spending €343 billion on defense in 2024 and planning for an additional €100 billion annually by 2027.5 Of the 5% NATO target, 1.5% is allocated to defense-linked critical infrastructure, addressing vulnerabilities in cybersecurity, communications networks, and other systems essential for modern military effectiveness.6
Only 18
of NATO’s 32 members met the 2% GDP defense spending target in 2024.7
2024 Defense Spending and Required Increases to Meet 5% GDP Target8
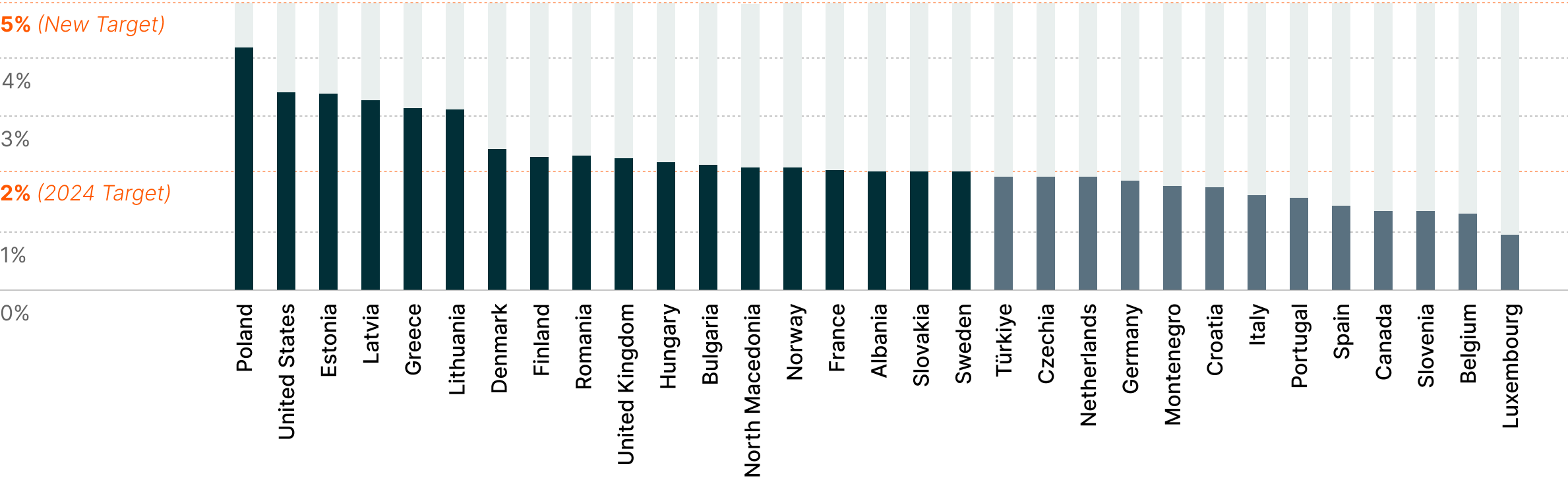
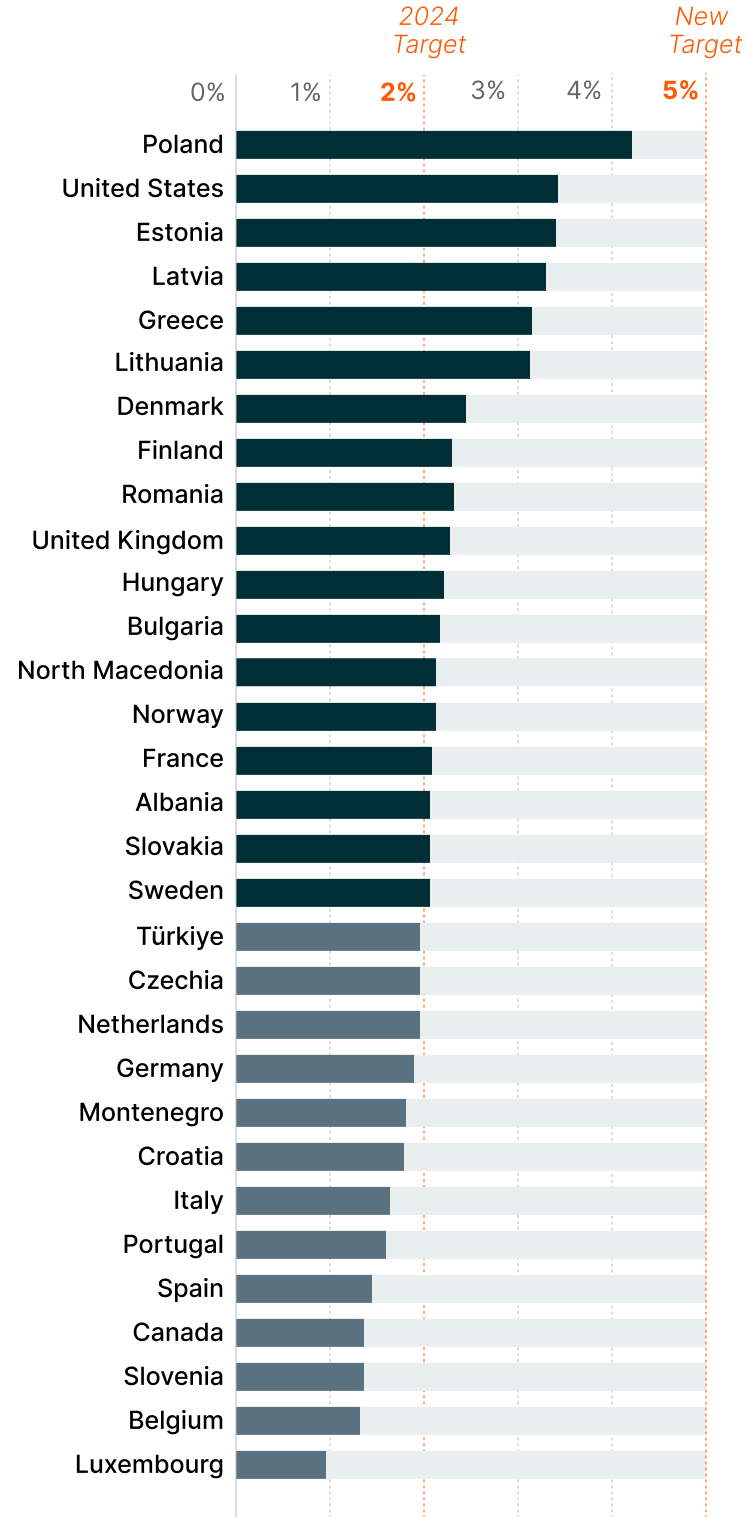
Technological Solutions Anchor the Next Phase of Defense Investment
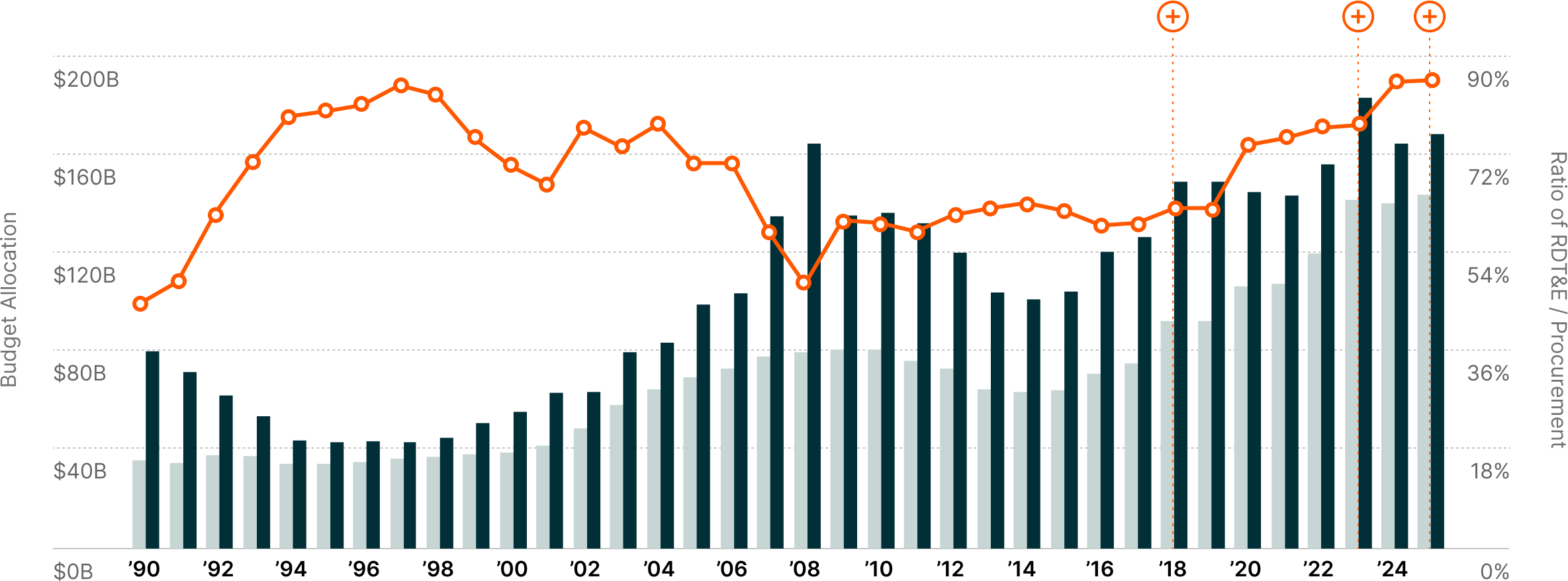
Defense budgets are evolving to incorporate digital modernization and cutting-edge technologies alongside investments in personnel and traditional equipment. The United States proposed $179 billion for RDT&E (Research, Development, Test, and Evaluation), as part of its 2026 defense budget request, a 27% YoY increase.9
The Pentagon’s technology integration reflects this shift. The Defense Innovation Unit scaled its budget to nearly $1 billion in 2024, up from approximately $200 million in the year prior, aiming to speed prototypes into production to meet the country’s defense modernization goals.10
U.S. Defense Procurement vs. RDT&E Spending11
EXPERT TAKEAWAY
“The global defense supercycle has just begun. Technology is emerging as the new military deterrent, driving growth in AI, drones, and autonomous systems. Cybersecurity, a critical layer of security, remains underinvested. This shift is only accelerating, and it’s set to redefine the defense industry in the years ahead.”
CASE STUDY
Leidos
Unmanned surface vessels, such as Sea Archer, are helping the U.S. Navy expand its reach, speed, and flexibility.
Unmanned surface vessels such as Sea Archer are helping the US Navy expand its reach, speed, and flexibility.






